Introduction
Installation
Guides
- Engine
- Profile
- Browser
- BrowserView
- Navigation
- Content
- Context menu
- DOM
- JavaScript
- Pop-ups
- Dialogs
- Downloads
- Chrome extensions
- Network
- Cache
- Cookies
- Proxy
- Authentication
- Permissions
- Plugins
- Printing
- Passwords
- User data profiles
- Credit cards
- Media
- Zoom
- Spell checker
- Deployment
- Chromium
Troubleshooting
Migration
Content
DotNetBrowser displays the content of various types, for example, images, video, PDF, and other, but in most cases you will display the HTML content of a web page. This guide shows how to access web page content, get the currently selected text, find some text on a web page, save the web page as a file or a set of files, and other actions.
Content size
By default, the IBrowser size is empty. Many web pages rely on this size and require it not to be empty. Otherwise, the layout of the DOM document cannot be parsed and displayed at all.
If you do not need to display the content of a loaded web page, but the page should “think” it is loaded in an IBrowser with a non-empty size, set the size programmatically using the IBrowser.Size property.
Accessing HTML
To get a string that represents HTML of an IFrame, use the IFrame.Html property.
It is recommended to use this property only when the whole web page or a particularIFrame is loaded completely. Otherwise, you may receive an incomplete HTML or an empty string.
The following example demonstrates how to print HTML of the currently loaded main IFrame:
Console.WriteLine(browser.MainFrame?.Html);
Console.WriteLine(browser.MainFrame?.Html)
Accessing selection
To get selection on the currently loaded IFrame as HTML, use the IFrame.SelectedHtml property:
string selectionAsHtml = frame.SelectedHtml;
Dim selectionAsHtml As String = frame.SelectedHtml
If you only need to get the selected text without the selection’s HTML, use the IFrame.SelectedText property as shown in the code sample below:
string selectionAsText = frame.SelectedText;
Dim selectionAsText As String = frame.SelectedText
Finding text
DotNetBrowser allows you to find text on the currently loaded web page and highlight all the matches.
DotNetBrowser searches text only through the visible content of the loaded web pages which have non-empty size.
To perform the search on the currently loaded web page, use the ITextFinder interface:
ITextFinder textFinder = browser.TextFinder;
Dim textFinder As ITextFinder = browser.TextFinder
The following example demonstrates how to find the “text” on the currently loaded web page with the specified search parameters and wait until the search is completed:
private const string Html = "<html><body><p>Find me</p><p>Find me</p></body></html>";
public static void Main()
{
using (IEngine engine = EngineFactory.Create())
{
using (IBrowser browser = engine.CreateBrowser())
{
browser.Size = new Size(700, 500);
byte[] htmlBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Html);
browser.Navigation
.LoadUrl($"data:text/html;base64,{Convert.ToBase64String(htmlBytes)}")
.Wait();
// Add a timeout to make sure the web page is rendered completely.
Thread.Sleep(2000);
// Find text from the beginning of the loaded web page.
string searchText = "find me";
IHandler<FindResultReceivedParameters> intermediateResultsHandler =
new Handler<FindResultReceivedParameters>(ProcessSearchResults);
Console.WriteLine("Find text (1/2)");
ITextFinder textFinder = browser.TextFinder;
FindResult findResult =
textFinder.Find(searchText, null, intermediateResultsHandler)
.Result;
int selectedMatch = findResult.SelectedMatch;
int count = findResult.NumberOfMatches;
Console.WriteLine($"Find Result: {selectedMatch}/{count}");
Console.WriteLine("Find text (2/2)");
findResult = textFinder
.Find(searchText, null, intermediateResultsHandler)
.Result;
selectedMatch = findResult.SelectedMatch;
count = findResult.NumberOfMatches;
Console.WriteLine($"Find Result: {selectedMatch}/{count}");
textFinder.StopFinding();
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to terminate...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static void ProcessSearchResults(FindResultReceivedParameters args)
{
FindResult result = args.FindResult;
if (args.IsSearchFinished)
{
Console.WriteLine("Found: "
+ result.SelectedMatch
+ "/"
+ result.NumberOfMatches);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Search in progress... Found "
+ result.SelectedMatch
+ "/"
+ result.NumberOfMatches);
}
}
Private Const Html As String = "<html><body><p>Find me</p><p>Find me</p></body></html>"
Public Shared Sub Main()
Using engine As IEngine = EngineFactory.Create()
Using browser As IBrowser = engine.CreateBrowser()
browser.Size = New Size(700, 500)
Dim htmlBytes() As Byte = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Html)
browser.Navigation.
LoadUrl($"data:text/html;base64,{Convert.ToBase64String(htmlBytes)}").
Wait()
' Add a timeout to make sure the web page is rendered completely.
Thread.Sleep(2000)
' Find text from the beginning of the loaded web page.
Dim searchText = "find me"
Dim intermediateResultsHandler As IHandler(Of FindResultReceivedParameters) =
New Handler(Of FindResultReceivedParameters)(
AddressOf ProcessSearchResults)
Console.WriteLine("Find text (1/2)")
Dim textFinder As ITextFinder = browser.TextFinder
Dim findResult As FindResult =
textFinder.Find(searchText, Nothing, intermediateResultsHandler).
Result
Dim selectedMatch = findResult.SelectedMatch
Dim count = findResult.NumberOfMatches
Console.WriteLine($"Find Result: {selectedMatch}/{count}")
Console.WriteLine("Find text (2/2)")
findResult = textFinder.
Find(searchText, Nothing, intermediateResultsHandler).
Result
selectedMatch = findResult.SelectedMatch
count = findResult.NumberOfMatches
Console.WriteLine($"Find Result: {selectedMatch}/{count}")
textFinder.StopFinding()
End Using
End Using
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to terminate...")
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub
Private Shared Sub ProcessSearchResults(args As FindResultReceivedParameters)
Dim result As FindResult = args.FindResult
If args.IsSearchFinished Then
Console.WriteLine(
$"Found: {result.SelectedMatch}/{result.NumberOfMatches}")
Else
Console.WriteLine(
$"Search in progress... Found {result.SelectedMatch}/{result.NumberOfMatches}")
End If
End Sub
The search matches are written down as shown below:
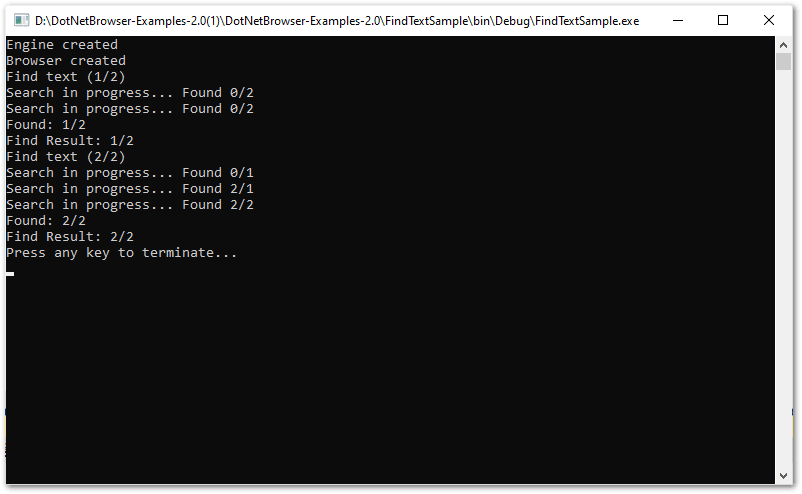
The complete example is available in our repository: C#, VB.NET.
Canceling search
To clear the highlighted search results on a web page and cancel the search, use the ITextFinder.StopFinding() method.
The StopFindAction parameter of this method is an action to be applied to the current selection on the web page. By default, this is StopFindAction.ClearSelection.
For example:
textFinder.StopFinding();
textFinder.StopFinding()
Saving a web page
DotNetBrowser allows to save a web page as a file or a set of files. It is done using the IBrowser.SaveWebPage(string, string, SavePageType) method which accepts these parameters:
- A string with a name of the target file;
- A string with the directory path to save page resources;
- A type of the save operation (
SavePageType).
For example:
string filePath = Path.GetFullPath("SavedPages\\index.html");
string dirPath = Path.GetFullPath("SavedPages\\resources");
Directory.CreateDirectory(dirPath);
if (browser.SaveWebPage(filePath, dirPath, SavePageType.CompletePage)) {
Console.WriteLine("The web page has been saved to " + filePath);
} else {
Console.WriteLine("Failed to save the web page to " + filePath);
}
Dim filePath As String = Path.GetFullPath("SavedPages\index.html")
Dim dirPath As String = Path.GetFullPath("SavedPages\resources")
Directory.CreateDirectory(dirPath)
If browser.SaveWebPage(filePath, dirPath, SavePageType.CompletePage) Then
Console.WriteLine("The web page has been saved to " & filePath)
Else
Console.WriteLine("Failed to save the web page to " & filePath)
End If
Taking bitmap of a web page
The library allows you to take a bitmap that contains the pixels of the currently loaded web page. The bitmap size equals to the size of the IBrowser instance where the web page is loaded.
To get an image of a web page, we recommend performing the following actions:
- Resize the
IBrowserinstance to the required dimension (for example, 500x500). - Load a web page and wait until the main frame of the web page is loaded completely.
- Take the bitmap of the currently loaded web page.
- Convert the bitmap to the required format and save it.
The following example demonstrates how to do that:
// 1. Resize browser to the required dimension.
browser.Size = browserSize;
// 2. Load the required web page and wait until it is loaded completely.
Console.WriteLine("Loading https://html5test.teamdev.com");
browser.Navigation
.LoadUrl("https://html5test.teamdev.com")
.Wait();
// 3. Take the bitmap of the currently loaded web page. Its size will be
// equal to the current browser's size.
DotNetBrowser.Ui.Bitmap image = browser.TakeImage();
Console.WriteLine("Browser image taken");
// 4. Convert the bitmap to the required format and save it.
Bitmap bitmap = ToBitmap(image);
bitmap.Save("screenshot.png", ImageFormat.Png);
Console.WriteLine("Browser image saved");
' 1. Resize browser to the required dimension.
browser.Size = browserSize
' 2. Load the required web page and wait until it is loaded completely.
Console.WriteLine("Loading https://html5test.teamdev.com")
browser.Navigation.LoadUrl("https://html5test.teamdev.com").Wait()
' 3. Take the bitmap of the currently loaded web page. Its size will be
' equal to the current browser's size.
Dim image As Bitmap = browser.TakeImage()
Console.WriteLine("Browser image taken")
' 4. Convert the bitmap to the required format and save it.
Dim bitmap As Drawing.Bitmap = ToBitmap(image)
bitmap.Save("screenshot.png", ImageFormat.Png)
Console.WriteLine("Browser image saved")
The bitmap conversion to a .NET System.Drawing.Bitmap for further manipulations is demonstrated below:
public static Bitmap ToBitmap(DotNetBrowser.Ui.Bitmap bitmap)
{
int width = (int) bitmap.Size.Width;
int height = (int) bitmap.Size.Height;
byte[] data = bitmap.Pixels.ToArray();
Bitmap bmp = new Bitmap(width,
height,
PixelFormat.Format32bppRgb);
BitmapData bmpData = bmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, bmp.Width, bmp.Height),
ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, bmp.PixelFormat);
Marshal.Copy(data, 0, bmpData.Scan0, data.Length);
bmp.UnlockBits(bmpData);
return bmp;
}
Public Shared Function ToBitmap(bitmap As Bitmap) As Drawing.Bitmap
Dim width = CInt(bitmap.Size.Width)
Dim height = CInt(bitmap.Size.Height)
Dim data() As Byte = bitmap.Pixels.ToArray()
Dim bmp As New Drawing.Bitmap(width, height, PixelFormat.Format32bppRgb)
Dim bmpData As BitmapData = bmp.LockBits(
New Drawing.Rectangle(0, 0, bmp.Width, bmp.Height),
ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, bmp.PixelFormat)
Marshal.Copy(data, 0, bmpData.Scan0, data.Length)
bmp.UnlockBits(bmpData)
Return bmp
End Function
The complete example is available in our repository: C#, VB.
Settings
Using IBrowserSettings you can configure different content settings for a single IBrowser instance. These are some of the actions available:
- disable images, plugins, JavaScript, local storage, application cache;
- allow running insecure content or allow JavaScript access clipboard.
You can find the list of other supported settings in API specification.
Default encoding
To configure the default text encoding on a web page, use the code sample below:
browser.Settings.DefaultEncoding = "UTF-8";
browser.Settings.DefaultEncoding = "UTF-8"
JavaScript
By default, JavaScript is enabled on a web page. If you need to disable JavaScript, use the code sample below:
browser.Settings.JavaScriptEnabled = false;
browser.Settings.JavaScriptEnabled = False
Images
If you do not need to display images on a web page to reduce the network traffic, you can disable them using the code sample below:
browser.Settings.ImagesEnabled = false;
browser.Settings.ImagesEnabled = False
Color scheme
By default, DotNetBrowser respects OS color scheme and changes the page appearance to dark or light tone (if the corresponding functionality is implemented by website owner).
You can also force the required color scheme. See code below:
// Sets dark color scheme for particular Browser instance.
browser.Settings.PreferredColorScheme = PreferredColorScheme.Dark;
// Sets light color scheme for particular Browser instance.
browser.Settings.PreferredColorScheme = PreferredColorScheme.Light;
' Sets dark color scheme for particular Browser instance.
browser.Settings.PreferredColorScheme = PreferredColorScheme.Dark
' Sets light color scheme for particular Browser instance.
browser.Settings.PreferredColorScheme = PreferredColorScheme.Light
Default background color
When Chromium does not know the background color of a web page, or the color has not been specified at all, it uses the white color for about:blank page. It may result in a kind of white flickering when you load a website in a different color accent. For example, you have a website in purple tone, and when it is loaded in DotNetBrowser: first white background is shown and then your website appears. This situation can be eliminated by setting the matching color background. See an example below:
Color purple = new Color(0.6f, 0.3f, 0.6f);
browser.Settings.DefaultBackgroundColor = purple;
Dim purple As New Color(0.6F, 0.3F, 0.6F)
browser.Settings.DefaultBackgroundColor = purple

Plugins
You can filter the installed plugins. If you need to disable all plugins on a web page, use the following approach:
browser.Settings.PluginsEnabled = false;
browser.Settings.PluginsEnabled = False
Local storage
By default, local WebStorage is enabled. To disable it and prevent JavaScript from storing data in the local storage, use the following setting:
browser.Settings.LocalStorageEnabled = false;
browser.Settings.LocalStorageEnabled = False
Scrollbars
You may want to hide scrollbars on a web page when taking bitmap of a web page or inside Kiosk applications. Use the following setting:
browser.Settings.ScrollbarsHidden = true;
browser.Settings.ScrollbarsHidden = True
Once you call this method, the web pages loaded in the IBrowser instance does not display scrollbars anymore.
Web storage
DotNetBrowser allows to access and work with JavaScript Web Storage that provides mechanisms to store key/value pairs in more intuitive way than using cookies.
There are two types of the Web Storage:
-
sessionStoragemaintains a separate storage area for each given origin that is available during the page session; -
localStoragedoes the same thing but persists even if the browser is closed and reopened.
To access the session and local Web Storage, use the following code sample:
IWebStorage sessionStorage = frame.SessionStorage;
IWebStorage localStorage = frame.LocalStorage;
Dim sessionStorage As IWebStorage = frame.SessionStorage
Dim localStorage As IWebStorage = frame.LocalStorage
The localStorage can be disabled. In this case, the IWebStorage methods throw the WebStorageSecurityException.
Code sample below demonstrates how to place an item to the localStorage using DotNetBrowser
WebStorage API:
localStorage["Name"] = "Tom";
localStorage("Name") = "Tom"
You can access the inserted item in JavaScript using the following code:
window.localStorage.Name; // <- Returns "Tom"
Editor commands
Editor commands are the commands for text manipulation when editing in a text field, text area, or WYSIWYG editor. Also, these commands include more common commands like Cut, Copy, Paste, SelectAll, Undo, Redo which can be executed for the frame on the loaded web page.
The editor commands can be executed as shown in the code sample below:
browser.Navigation.LoadUrl("http://www.google.com").Wait();
// Inserts "TeamDev DotNetBrowser" text into Google Search field.
browser.MainFrame.Execute(EditorCommand.InsertText("TeamDev DotNetBrowser"));
// Inserts a new line into Google Search field to simulate Enter.
browser.MainFrame.Execute(EditorCommand.InsertNewLine());
browser.Navigation.LoadUrl("https://www.google.com").Wait()
' Inserts "TeamDev DotNetBrowser" text into Google Search field.
browser.MainFrame.Execute(EditorCommand.InsertText("TeamDev DotNetBrowser"))
' Inserts a new line into Google Search field to simulate Enter.
browser.MainFrame.Execute(EditorCommand.InsertNewLine())
WebSockets
DotNetBrowser supports web pages that use WebSockets technology: